
Zestaw obrazów 2019
zdjecie1.jpg
zdjecie2.jpg
zdjecie3.jpg
zdjecie4.jpg
zdjecie5.jpg
zdjecie6.jpg
2019_1.JPG
2019_2.JPG
2019_4.JPG
Światowe
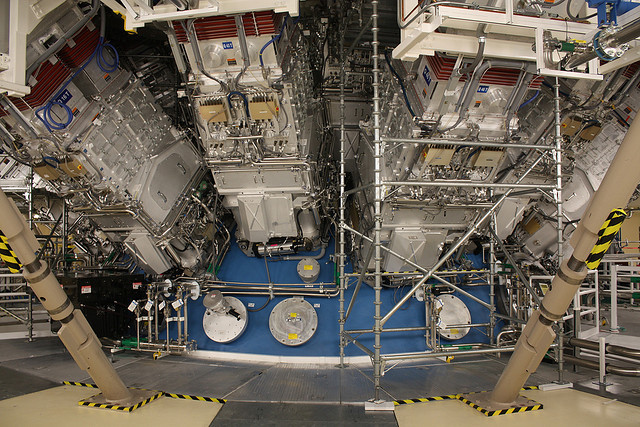 A crucial milestone has been reached by US lab researchers in their quest towards cracking self-sustaining nuclear fusion.
A crucial milestone has been reached by US lab researchers in their quest towards cracking self-sustaining nuclear fusion.
Harnessing fusion, the process powering the sun, has the potential to create an abundant source of low-cost energy. Despite being the object of significant study, it has so far remained elusive, as artificial fusion reactions created here on earth consume more energy than they produce. Following a breakthrough by the $35bn National Ignition Facility (NIF) in Livermore, California, there are new hopes of achieving a self-sustaining reaction, or ignition where the power output exceeds the power required to start the reaction.
Scientists at NIF reached the point of nuclear fusion by heating and compressing a small pellet of hydrogen fuel using 192 beams from the world’s most powerful laser. According to a recent update, one NIF experiment in late September resulted in the amount of energy being produced through the fusion reaction exceeding the amount of energy consumed by the fuel for the first time in any facility in the world.
‘Promising’ breakthrough demonstration
NIF is yet to reach the point of ‘ignition’, a self-sustaining reaction where the amount of energy produced exceeds the energy supplied to the laser. This delay in research is known to be due to inefficiencies in the system, meaning that most of the energy delivered by the lasers is lost in the effort to achieve the temperatures required for fusion, rather than on the reaction itself. However, this latest breakthrough in fusion is the most promising in recent years, moving fusion research forward significantly.
It has been hoped that the NIF would make a breakthrough after almost half a century of striving towards this goal. The NIF team announced a plan in 2009 to demonstrate nuclear fusion providing net energy by the 30th September 2012. However, this deadline was unmet due to technical errors, and the output was less than that predicted by mathematical models. Later, the facility shifted its focus from fusion to nuclear weapons, part of its original purpose.
Nevertheless, the latest experiment’s results are in keeping with output predictions, which is encouraging both for future ignition research at NIF, and for general advocates of nuclear fusion.
Current nuclear power operates on the concept of nuclear fission, which is the splitting of the atom, rather than the fusing of the atom. NIF is one of several fusion research projects worldwide that are conducting research into nuclear fusion. One such project is the multi-billion pound ITER facility which is being constructed in Cadarache, France. In contrast with the NIFs approach to fusion, ITER aims to use the concept of ‘magnetic confinement’ to contain fusion fuel within a magnetic field. The Nuclear Power Plant Generation The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is an example of the current use of nuclear power. Located in the Futaba District of Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. This plant has been disabled since it was hit by the magnitude 9.0 earthquake and tsunami on the 11th March in 2011.
Recently, an isotope ratio analysis of 235U and 238U in the soil was performed using ICP-MS, which you can read in this article: Soil Survey Related to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant Accident. After the disaster, the Japanese government had planned to gradually reduce its dependence on nuclear power. However, Japan has since revised their nuclear power plan and a new energy policy has been approved which will see nuclear generation continue.
Source: Pollution Solutions
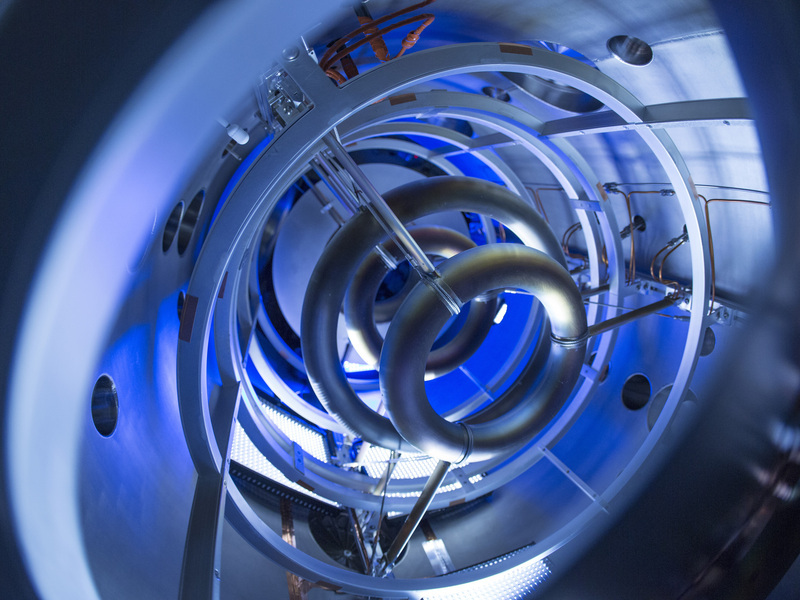 Lockheed Martin’s compact reactor concept / fusion drives for aircraft and trucks?
Lockheed Martin’s compact reactor concept / fusion drives for aircraft and trucks?
Building a small, transportable fusion power plant has long been a dream of fusion researchers. In the course of their research, however, it became clear that a functioning power plant has to be of a certain minimum size. Nevertheless, there are occasionally renewed attempts (see “The fusion upstarts”, in Nature, Vol. 511, 14/7/2014, p. 398 ff.). IPP scientists Professor Sibylle Günter and Professor Karl Lackner explain why also the latest version proposed by US technology concern Lockheed Martin might well remain a dream:
The patent applications for the device proposed by Lockheed Martin do not involve a really new concept, but combine the known concepts of a magnetic cusp and a magnetic mirror. Both are impaired by the fact that charged particles can escape along the magnetic field lines out of the confinement region. This leads to an intolerable energy loss, because it is primarily the fast, hot particles that get lost first. Nor does it help here, as proposed, to link several cusps behind one another or combine them with magnetic mirrors.
What is envisaged is incorporating coils in the vessel, i.e. inside the plasma. This needs connections to the outside and fixtures in the plasma vessel. Hot plasma particles from the core of the device would thus come into direct contact with these fixtures. The fundamental idea of magnetic confinement, however, is precisely to keep the high-energy plasma particles in the core moving along the magnetic field lines at always the same volume without impinging on material walls. Otherwise the plasma cools down very fast. One solution here would be superconducting coils levitating in the vessel without support, this leaving, however, the above energy loss problem: The configuration proposed is not suitable for confining hot plasmas.
Furthermore, the coils inside the plasma vessel have to be shielded not only from the surrounding hot plasma, but also from the neutrons produced in the fusion process. With superconducting coils, at least 80 centimetres of shielding around each coil is needed. This does not accord with the power plant size envisaged.
All of these problems have been resolved by the tokamak and stellarator concepts pursued today. Nevertheless, it is not possible to build small, transportable power plants. This is because attaining a positive energy balance, i.e. producing more fusion power than needed for heating the plasma, calls for extremely good thermal insulation of the plasma, viz. about 50 times better than styropor. In a power plant a temperature in the plasma core of 100 to 200 million degrees is needed, while at the walls no more than 1,000 degrees is tolerable. Such large temperature differences in the plasma drive turbulent flows that mix hot and cold regions with one another, i.e. impair the thermally insulating effect of the magnetic field. This has to be compensated with a larger volume. Here it is the size of the temperature gradient that determines the turbulent flows and hence the minimum size of a power plant. How a positive energy balance is to be achieved with the compact version propagated by Lockheed Martin is not even remotely mentioned in the patent applications.
Source: Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik
 Lockheed Martin's project to create a compact fusion reactor could provide a boost for other ventures aiming to harness nuclear fusion energy on a small scale — or at least they hope so.
Lockheed Martin's project to create a compact fusion reactor could provide a boost for other ventures aiming to harness nuclear fusion energy on a small scale — or at least they hope so.
"I'm glad to see them pursuing high-pressure plasma, because it's the only logical way to have an economical fusion reactor," Jaeyoung Park, president and chief scientist at New Mexico-based EMC2 Fusion Development Corp., told NBC News on 16 October. "Life is lonely if you're the only one doing it."
EMC2 Fusion has been working on a concept similar to Lockheed Martin's for years, as a follow-up to decades' worth of research by physicist Robert Bussard. The company is just one of a myriad of ventures aiming to turn nuclear fusion, the reaction that powers the sun as well as hydrogen bombs, into a commercial power-generating technology.
If fusion could be commercialized, it would offer a new kind of always-on power source that's cleaner than nuclear fission and fossil fuels, and potentially be cheaper than coal.
Some fusion research efforts are getting millions or even billions of dollars in government support — including the Z Machine at Sandia National Laboratories in New Mexico; the $3.5 billion laser-blasting National Ignition Facility in California; and the international ITER experimental project in France, which has a price tag that estimates say could rise as high as $50 billion over the next decade.
Other ventures, such as EMC2 Fusion and Lockheed Martin's newly revealed T4 project, aim to commercialize fusion for far less, using far less orthodox technological approaches.
Fusion reactor on a truck?
Over the past few years, the Navy spent $12 million to support EMC2 Fusion's research — and now EMC2 Fusion, like Lockheed, is looking for support from investors and other partners to take their experiments to the next level. In EMC2 Fusion's case, that means finding roughly $30 million for a demonstration reactor that shows how its Polywell concept could scale up to a net energy gain, and eventually commercial-scale reactors.
"We are getting decent exposure," Park said in an email. "This has helped us to make progress in our fundraising. It is moving forward, and I am cautiously optimistic about the chance of getting funded for the next phase, though everything takes a lot longer than expected. It is certainly an exciting roller coaster ride for a scientist." Another couple of months could tell the tale, Park said. And it doesn't hurt that the leader of Lockheed Martin's compact fusion research team, Tom McGuire, said his concept has some similarities to EMC2 Fusion's Polywell, which involves shooting positive ions into a powerful electromagnetic field. "I am happy to see the core principle of the Polywell concept is being adopted by others for their efforts for economical fusion power," Park said.
'The race is on'
Park's not the only one: Lockheed Martin's news was also cheered on the Talk-Polywell discussion forum, where members delve into the nitty-gritty of unorthodox fusion physics. "The race is on to achieve major funding for this general approach," one commenter wrote.
Lockheed Martin is by far the biggest company to reveal its interest in creating compact fusion reactors, and the fact that it's looking for partners should add to the already-percolating interest in commercial fusion research. Amazon.com billionaire Jeff Bezos, for instance, is one of the investors in Canada-based General Fusion. Meanwhile, Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen has invested in California-based Tri-Alpha Energy.
Other ventures such as Lawrenceville Plasma Physics are flying relatively under the radar but aiming for big breakthroughs in fusion physics.
Helion Energy, a start-up that was spun off from a University of Washington fusion research project, is working on its own demonstration fusion reactor — and recently announced a $1.5 million venture capital infusion.
Lockheed Martin's McGuire said his team would build a prototype compact fusion reactor within five years, but Helion's schedule is even more ambitious: The company's CEO, David Kirtley, hopes to get to the break-even point — that is, a fusion reaction where the energy output exceeds the input — within three years. In a recent email, Kirtley said Helion was making good progress toward that goal. "We have increased our demonstrated plasma temperatures to over 5 KeV [5,000 electron volts] and continue work on the engineering hardware of our next, break-even machine," he said.
So who'll win the commercial fusion race? Will anyone ever cross the break-even line and turn fusion into a cheap power source? Stay tuned ... at least it's good to know there's a race.
Source: NBC News
 The floor upon which the biggest fusion machine in the world will rely on has been constructed.
The floor upon which the biggest fusion machine in the world will rely on has been constructed.
This landmark achievement marks the conclusion of the works that started in August 2010 and represent an investment of around 100 million EUR for F4E, the European Union’s organisation responsible for Europe’s contribution to ITER. The construction has been carried out by a group of companies led by GTM SUD and under the supervision of F4E and the ENGAGE consortium consisting of Assystem, Atkins, Empresarios Agrupados and Egis. The floor will be able to support more than 400,000 tonnes of buildings infrastructure and equipment, including the ITER machine weighing 23,000 tonnes.
Professor Henrik Bindslev, Director of Fusion for Energy (F4E), explained that “Europe is taking the ITER construction to the next level. The basemat is the test bed of the biggest international collaboration in the field of energy. It’s where the scientific work and industrial know-how will come together and be deployed to seize the power of fusion energy”. Professor Osamu Motojima, Director General of ITER International Organization (ITER IO) stated that “the conclusion of this task is a historical moment for the project. Years of hard work by all ITER parties are bearing fruit as the facility takes shape and makes progress on all fronts”.
The ITER basemat in figures:
The basemat is far more complex that it seems. It has a surface of 9,600m2 and a thickness of 1,5 m of reinforced concrete consisting of four successive layers - two of 50cm, one of 30cm and one of 20cm. The first of the fifteen plots of concrete was poured in December 2013. Following the approval of the French Nuclear Authority in July 2014, regarding the robustness of the building design, nine central sections of the slab were poured within seven weeks leading to a successful completion of the works in late August 2014. In total 150 workers were involved in this operation, using 14,000m3 of concrete, 3,600 tonnes of steel and 2,500 embedded plates.
A web of 493 plinths coated with pads, lies beneath the upper slab, able to absorb the effect of an intense seismic shock. More concrete and thick steel rebars form a mesh to keep the foundations stable and lift the immense load of the machine. The design and validation process have been extremely challenging because the basemat will be the floor of the Tokamak building that will house the machine and shield it. For this reason it is has been subjected to heavy scrutiny from ITER IO and the French Nuclear Regulator. The infrastructure fully complies with the set of nuclear safety requirements branding ITER as the biggest nuclear facility in France and the first ever nuclear fusion facility in the world.
How will the ITER site evolve?
With the ITER basemat now completed, the construction of the complex that will house the core buildings of the machine has started. The VFR consortium, consisting of VINCI Construction Grands Projets, Ferrovial Agroman, Razel-Bec, Dodin Campenon Bernard, Campenon Bernard Sud-Est, GTM Sud and Chantiers Modernes Sud are responsible for carrying out the works. The building will be 80 metres tall, 120 metres long and 80 metres wide. It will require 16,000 tonnes of steel rebars and 150,000 m3 of concrete.
There has also been progress at the Assembly Hall building, where the massive ITER components will be put together. The steel structure of the building has become visible and so far the lower sections of the eight first columns have been erected. They weigh around 15 tonnes and are currently 12 metres high (once fully erected they will be 60 metres high).
The temporary road network, infirmary and restaurant have also completed making it possible for the contractors to set up their company offices on the site.
Source: Fusion for Energy
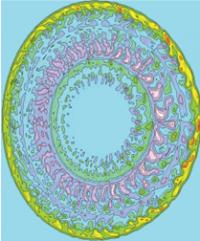 Recent fusion experiments on the DIII-D tokamak at General Atomics (San Diego) and the Alcator C-Mod tokamak at MIT (Cambridge, Massachusetts), show that beaming microwaves into the center of the plasma can be used to control the density in the center of the plasma, where a fusion reactor would produce most of its power. Several megawatts of microwaves mimic the way fusion reactions would supply heat to plasma electrons to keep the "fusion burn" going.
Recent fusion experiments on the DIII-D tokamak at General Atomics (San Diego) and the Alcator C-Mod tokamak at MIT (Cambridge, Massachusetts), show that beaming microwaves into the center of the plasma can be used to control the density in the center of the plasma, where a fusion reactor would produce most of its power. Several megawatts of microwaves mimic the way fusion reactions would supply heat to plasma electrons to keep the "fusion burn" going.
The new experiments reveal that turbulent density fluctuations in the inner core intensify when most of the heat goes to electrons instead of plasma ions, as would happen in the center of a self-sustaining fusion reaction. Supercomputer simulations closely reproduce the experiments, showing that the electrons become more turbulent as they are more strongly heated, and this transports both particles and heat out of the plasma.
"We are beginning to uncover the fundamental mechanisms that control the density, under conditions relevant to a real fusion reactor," says Dr. Darin Ernst, a physicist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, who led the experiments and simulations, together with co-leaders Dr. Keith Burrell (General Atomics), Dr. Walter Guttenfelder (Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory), and Dr. Terry Rhodes (UCLA).
The experiments were conducted by a team of researchers as part of a National Fusion Science Campaign. This new program enables research on one fusion experiment to be expanded to device another with complementary instrumentation and capabilities. "The National Campaign has increased the impact of our work, with added benefit to the fusion program," says Dr. Ernst. "Comparing Alcator C-Mod and DIII-D tests our new predictions that particle collisions strongly reduce this type of turbulence. The collision rate varies by a factor of ten between the two machines," says Ernst.
The experiments and simulations suggest that trapped electron turbulence becomes more important under the conditions expected in self-heated fusion reactors. The structure of the simulated turbulence during the electron heating is shown at right. The simulations closely matched detailed measurements of the actual turbulence in the 20cm diameter inner core. "We discovered sheared flows also drive turbulence in the inner plasma core, but as we approached conditions where mainly the electrons are heated, the usual plasma flow is reduced and pure trapped electron turbulence begins to dominate," says Dr. Guttenfelder, who did the supercomputer simulations for the DIII-D experiments, along with Dr. Andris Dimits (LLNL). Measurements revealed a band of fluctuations, separated by a constant frequency interval, like harmonics in a musical note. "These new coherent fluctuations appear to be consistent with the basic trapped electron instability that grows stronger during heating, " says Dr. Rhodes.
In a self-heated fusion reactor, fusion reactions produce very energetic alpha particles that collide with electrons as they move through the plasma. The collisions heat the electrons by imparting random thermal motion. The electrons in turn collide with and heat cooler deuterium and tritium fuel ions to fusion temperatures. However, turbulent eddies can swirl the particles and energy away from the hot core toward the cooler edge, where they eventually are lost to the walls of the chamber.
These experiments are part of a larger systematic study of turbulent energy and particle loss under fusion-relevant conditions. "It's important to understand what drives the turbulence, and how it can be controlled and minimized, to find new ways of operating tokamaks that exploit that knowledge," says Dr. Burrell. By comparing detailed turbulence measurements with simulations, researchers hope to understand how turbulence controls the core temperature under fusion conditions.
Source: EurekAlert
Informacje z Kraju
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
GO4FUSION Capability Mapping Survey – termin do 21 stycznia 2026 r.
15-01-2026
Projekt GO4FUSION zaprasza europejskie organizacje działające w obszarze energii termojądrowej do udziału w badaniu Capability Mapping Survey (mapowanie kompetencji i potencjału). Celem ankiety jest przygotowanie kompleksowego przeglądu europejskich kompetencji w zakresie...
Czytaj więcejIFPiLM wspiera podopiecznych Centrum TPD "Helenów"
22-12-2025

Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego (IFPiLM) od wielu lat angażuje się w działania na rzecz podopiecznych Centrum Rehabilitacji, Edukacji i Opieki TPD „Helenów” w Warszawie. 9 grudnia...
Czytaj więcejNaukowcy z IFPiLM uczestniczyli w kampanii eksperymentalnej na laserze GEKKO XII
20-11-2025

W dniach 10–14 listopada 2025 r. zespół naukowców z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego (IFPiLM) w składzie: dr hab. Katarzyna Batani, dr Hanna Marchenko oraz dr...
Czytaj więcejZgłoś swój udział w 18. edycji Letniej Szkoły Fizyki Plazmy!
07-11-2025

Zapraszamy do udziału w 18. edycji Letniej Szkoły Fizyki Plazmy – Kudowa Summer School "Towards Fusion Energy", która odbędzie się 8–12 czerwca 2026 r. w Kudowie-Zdroju. Organizatorem wydarzenia jest Instytut...
Czytaj więcejOdszedł prof. dr hab. Zbigniew Kłos
05-11-2025
Z głębokim żalem zawiadamiamy, że 3 listopada 2025 roku zmarł prof. dr hab. Zbigniew Kłos – wybitny naukowiec, współtwórca i wieloletni dyrektor Centrum Badań Kosmicznych PAN. W latach 2008–2011 Profesor pełnił...
Czytaj więcejKonsultacje Strategic Research & Innovation Agenda (SRIA) – do 5 listopada 2025 r.
17-10-2025
Europejska Platforma Interesariuszy Fuzji Jądrowej (European Fusion Stakeholder Platform), powołana w ramach projektu GO4FUSION CSA, pracuje nad przygotowaniem Strategicznego Programu na rzecz przyszłego partnerstwa publiczno-prywatnego (PPP) w obszarze energii termojądrowej....
Czytaj więcejIFPiLM wziął udział w drugim spotkaniu technicznym w ramach projektu DONES Con-P1
17-10-2025
Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) wziął udział w drugim spotkaniu technicznym realizowanym w ramach projektu DONES Consolidation Phase 1 (DONES ConP1) współfinansowanego przez Komisję Europejską w ramach programu...
Czytaj więcejProf. Jan Badziak z IFPiLM w gronie World's Top 2% Scientists
15-10-2025
Prof. dr hab. Jan Badziak z Zakładu Fizyki Plazmy Laserowej i Gęstej Plazmy Namagnetyzowanej w Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy znalazł się na prestiżowej liście Stanford/Elsevier Top 2% Scientists...
Czytaj więcej29. Festiwal Nauki z udziałem IFPiLM
10-10-2025

Podczas 29. Festiwalu Nauki w Warszawie, który odbył się w dniach 19–28 września 2025 roku, naukowcy z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy przeprowadzili lekcje dla uczniów klas 7–8 szkół...
Czytaj więcejPLASMA 2025 i 20-lecie Asocjacji Euratom–IFPiLM – podsumowanie wydarzenia
26-09-2025

W dniach 15–19 września 2025 roku w Warszawie odbyła się międzynarodowa konferencja naukowa PLASMA 2025 – International Conference on Research and Application of Plasmas, poświęcona badaniom, diagnostyce i zastosowaniom plazmy....
Czytaj więcejZ żalem żegnamy Profesora Jerzego Wołowskiego
25-09-2025

Z głębokim smutkiem przyjęliśmy wiadomość o śmierci prof. dr. hab. Jerzego Wołowskiego (1936–2025), wybitnego fizyka, wieloletniego pracownika Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy, mentora i przyjaciela. Jerzy Wołowski urodził się w...
Czytaj więcej20. rocznica Asocjacji Euratom-IFPiLM (CeNTE): Obchody dwóch dekad koordynacji badań nad syntezą jądrową
16-09-2025

19 września 2025 roku, podczas międzynarodowej Konferencji PLASMA 2025 odbywającej się w Warszawie i poświęconej badaniom, diagnostyce i zastosowaniom plazmy, IFPiLM będzie obchodzić 20. rocznicę koordynacji badań nad syntezą jądrową...
Czytaj więcejUdział IFPiLM w 49. Zjeździe Fizyków Polskich w Katowicach
13-09-2025
Podczas 49. Zjazdu Fizyków Polskich, który odbył się w dniach 5–11 września 2025 roku w Katowicach, Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) był reprezentowany zarówno w gronie prelegentów, jak...
Czytaj więcejProf. Agata Chomiczewska powołana na zastępcę dyrektora ds. naukowych w IFPiLM
03-09-2025

Informujemy, że Minister Energii Miłosz Motyka z dniem 1 września 2025 roku powołał dr hab. Agatę Chomiczewską na stanowisko zastępcy dyrektora do spraw naukowych w Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej...
Czytaj więcejPubliczna obrona rozprawy doktorskiej mgr. inż. Przemysława Tchórza - 21 sierpnia 2025 roku
15-07-2025
Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego zaprasza na publiczną obronę rozprawy doktorskiej mgr. inż. Przemysława Tchórza, która odbędzie się 21 sierpnia 2025 r. (czwartek) o godz. 12:00...
Czytaj więcejZawiadomienie o publicznej obronie rozprawy doktorskiej mgr. inż. Przemysława Tchórza
10-07-2025
Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego zaprasza na publiczną obronę rozprawy doktorskiej mgr. inż. Przemysława Tchórza, która odbędzie się 21 sierpnia 2025 r. (czwartek) o godz. 12:00...
Czytaj więcejHistoryczne wydarzenie – Rada Naukowa Instytutu nadała stopień doktora habilitowanego
10-07-2025
Po raz pierwszy w historii Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego (IFPiLM) Rada Naukowa podjęła uchwałę w sprawie nadania stopnia doktora habilitowanego. Było to możliwe dzięki uzyskaniu...
Czytaj więcejNowy skład Rady Oddziału Fizyki Plazmy Europejskiego Towarzystwa Fizycznego
04-07-2025

W pierwszym kwartale 2025 roku przeprowadzono wybory do Rady Oddziału Fizyki Plazmy Europejskiego Towarzystwa Fizycznego (EPS Plasma Physics Division). Sześciu kandydatów z najwyższą liczbą głosów zostało wybranych do Zarządu, a...
Czytaj więcejOgłoszenie o postępowaniu konkursowym na stanowisko zastępcy dyrektora do spraw naukowych
30-06-2025
OGŁOSZENIE o postępowaniu konkursowym na stanowisko zastępcy dyrektora do spraw naukowychw Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego w Warszawie Działając na podstawie art. 27 ust. 1 ustawy z dnia...
Czytaj więcejZawiadomienie o kolokwium habilitacyjnym
30-06-2025
ZAWIADOMIENIE o kolokwium habilitacyjnym Dnia 4 lipca 2025 r. o godz. 11:00 odbędzie się kolokwium habilitacyjne dr Katarzyny Batani (Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy) w trybie hybrydowym. Określenie osiągnięcia będącego podstawą ubiegania...
Czytaj więcejNaukowcy z IFPiLM dzielą się wiedzą specjalistyczną w zakresie fuzji na 10. Kongresie Przemysłu Jądrowego Europy Środkowej i Wschodniej 2025
12-06-2025
Naukowcy z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) – dr inż. Natalia Wendler i dr inż. Paweł Gąsior – wzięli udział w panelu dyskusyjnym podczas 10. Kongresu Przemysłu Jądrowego...
Czytaj więcejIFPiLM na 3. Kongresie "Nauka dla Społeczeństwa"
29-05-2025

W dniach 25-26 maja 2025 roku w Dużej Auli Politechniki Warszawskiej odbyła się 3. edycja Kongresu "Nauka dla Społeczeństwa". Celem wydarzenia było pokazanie, że nauka to nie tylko praca w...
Czytaj więcejZaproszenie na 3. edycję Kongresu „Nauka dla Społeczeństwa” z udziałem IFPiLM
22-05-2025

W dniach 25–26 maja 2025 roku na terenie Politechniki Warszawskiej odbędzie się 3. edycja Kongresu „Nauka dla Społeczeństwa” – wydarzenia, które pokazuje, że nauka to nie tylko praca w laboratoriach,...
Czytaj więcejZapraszamy na 28. Piknik Naukowy!
06-05-2025

Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) zaprasza w sobotę, 10 maja, na swoje stoisko podczas 28. Pikniku Naukowego, organizowanego przez Polskie Radio i Centrum Nauki Kopernik. Tegoroczna edycja wydarzenia,...
Czytaj więcejPorozumienie o współpracy pomiędzy IFPiLM a Narodowym Muzeum Techniki
18-04-2025

17 kwietnia 2025 roku zostało podpisane porozumienie o współpracy pomiędzy Narodowym Muzeum Techniki (NMT) a Instytutem Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM). Uroczyste spotkanie, z udziałem dyrektor IFPiLM dr hab. Moniki...
Czytaj więcejPolscy i francuscy naukowcy łączą siły w badaniach nad fuzją jądrową
28-03-2025

W dniach 24-25 marca 2025 roku w siedzibach IFJ PAN i Instytutu Francuskiego w Krakowie odbyło się spotkanie polsko-francuskie, którego celem była wymiana doświadczeń oraz rozwój współpracy naukowej między instytucjami...
Czytaj więcejGiełda Prac Magisterskich i Doktorskich w ELI ERIC
21-03-2025

Giełda Prac Magisterskich i Doktorskich w ELI ERIC (Extreme Light Infrastructure, European Research Infrastructure Consortium) Do: Magistrantów, Doktorantów i ich Promotorów, Miłośników ultrakrótkich impulsowych laserów dużej mocy i ich zastosowań, Entuzjastów egzotycznych zjawisk indukowanych...
Czytaj więcejOtwarcie likwidacji fundacji "Wspieranie Międzynarodowego Centrum Gęstej, Namagnesowanej Plazmy"
14-03-2025

OGŁOSZENIE O OTWARCIU LIKWIDACJI FUNDACJI "WSPIERANIE MIĘDZYNARODOWEGO CENTRUM GĘSTEJ, NAMAGNESOWANEJ PLAZMY"wraz z wezwaniem wierzycieli Podaje się do publicznej wiadomości, że w dniu 20 stycznia 2025 r. Rada Fundacji "WSPIERANIE MIĘDZYNARODOWEGO CENTRUM GĘSTEJ, NAMAGNESOWANEJ...
Czytaj więcejZapraszamy na międzynarodową konferencję na temat badań, diagnostyki i zastosowań plazmy – PLASMA 2025!
13-03-2025

Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) zaprasza na międzynarodową konferencję na temat badań, diagnostyki i zastosowań plazmy – PLASMA 2025, która odbędzie się w dniach 15-19 września 2025 roku...
Czytaj więcejSzkolenie online: "Granty na Eurogranty – jak przygotować skuteczny wniosek"
10-03-2025

Horyzontalne Punkty Kontaktowe Polska Wschodnia i Polska Centralna zapraszają na szkolenie online pt. "Granty na Eurogranty – jak przygotować skuteczny wniosek". "Granty na Eurogranty" to inicjatywa Polskiej Agencji Rozwoju Przedsiębiorczości (PARP)...
Czytaj więcejEksperymentalna sesja badawcza w laboratorium Plasma-Focus PF1000U w ramach współpracy ICDMP
27-02-2025
W dniach 10–21 lutego 2025 r. w laboratorium Plasma-Focus PF-1000U przeprowadzono sesję eksperymentalną, w której, obok zespołu IFPiLM, uczestniczył trzyosobowy zespół pracowników naukowych z Politechniki Praskiej (ČVUT), kierowany przez prof....
Czytaj więcejPaliwa termojądrowe wykryte podczas demonstracji lasera na JET
11-02-2025

Naukowcy i inżynierowie z ośmiu krajów, w tym z Polski, z powodzeniem zademonstrowali zastosowanie laserów na tokamaku Joint European Torus (JET), udowadniając, że jest to opłacalna technologia pomiaru retencji paliwa...
Czytaj więcejPracownik IFPiLM nominowany do tytułu Osobowość Roku w kategorii Nauka
24-01-2025
Pracownik badawczo-techniczny mgr inż. Olgierd Cichorek z Laboratorium Plazmowych Napędów Satelitarnych w IFPiLM został nominowany do tytułu Osobowość Roku 2024 w kategorii Nauka. Kapituła Redakcji „Polskiej Metropolii Warszawskiej”, „Echa Dnia” i...
Czytaj więcejProf. Monika Kubkowska nowym dyrektorem IFPiLM
02-01-2025

Z przyjemnością informujemy, że Pani Minister Przemysłu Marzena Czarnecka z dniem 1 stycznia 2025 roku powołała dr hab. Monikę Kubkowską na stanowisko dyrektora Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im....
Czytaj więcejChristian Perez von Thun członkiem grupy ITPA w obszarze Pedestal & Edge Physics
31-12-2024
Dr Christian Perez von Thun z Zakładu Badań Plazmy Termojądrowej w Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy został członkiem grupy International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA) w obszarze Pedestal & Edge...
Czytaj więcejPrzemysław Tchórz nowym co-Leaderem grupy roboczej WG2 w ramach COST Action PROBONO
23-12-2024

Przemysław Tchórz z Zakładu Fizyki i Zastosowań Plazmy Laserowej w Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy został mianowany w ramach konkursu co-Leaderem grupy roboczej WG2: Experiments: Proton boron and Towards...
Czytaj więcejIFPiLM wspiera podopiecznych z Centrum Rehabilitacji, Edukacji i Opieki TPD „Helenów”
20-12-2024

Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) od lat angażuje się w pomoc podopiecznym z Centrum Rehabilitacji, Edukacji i Opieki TPD „Helenów” w Warszawie. W 2024 roku wsparcie Instytutu miało...
Czytaj więcejWykład naukowców z IFPiLM podczas Śląskiego Festiwalu Nauki w Katowicach!
25-11-2024

Dr hab. Agata Chomiczewska i dr inż. Natalia Wendler z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) wygłoszą wykład pt. „Synteza jądrowa – przełomowe wyniki badań, które mogą zmienić przyszłość...
Czytaj więcejModernizacja diagnostyki PHA i udział naukowców z IFPiLM w nowej kampanii na W7-X
24-10-2024

Zespół naukowców z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) przeprowadził znaczącą modernizację diagnostyki PHA (pulse-height analyzer), która jest obecnie aktywnie wykorzystywana na stellaratorze Wendelstein 7-X w ramach kampanii OP.2.2,...
Czytaj więcejOGŁOSZENIE
22-10-2024
Ogłoszenie o postępowaniu konkursowym na stanowisko dyrektora w Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego Działając na podstawie art. 24 ust. 2 ustawy z dnia 30 kwietnia 2010 r....
Czytaj więcejOd powstania lasera do fuzji jądrowej – zapraszamy na wykład dr Agnieszki Zaraś-Szydłowskiej
21-10-2024

Zapraszamy na wykład dr Agnieszki Zaraś-Szydłowskiej z Zakładu Fizyki i Zastosowań Plazmy Laserowej. Temat wystąpienia: Od powstania lasera do fuzji jądrowej: technologia, zastosowania i najnowsze osiągnięcia w świecie laserów Spotkanie odbędzie się...
Czytaj więcejZapraszamy na wykład o plazmowych napędach kosmicznych
27-09-2024

Zapraszamy na wykład mgr. inż. Macieja Jakubczaka z Laboratorium Plazmowych Napędów Satelitarnych. Temat wystąpienia: Nadniebny rejs - historia i przyszłość plazmowych napędów kosmicznych. Spotkanie odbędzie się 3 października 2024 r. o godz....
Czytaj więcejEksperymenty z mieszaniną paliw fuzyjnych stabilizują plazmę w reaktorach fuzyjnych
25-09-2024
Przyszłe elektrownie termojądrowe mogą doświadczać mniejszych strat energii w spalanej plazmie niż dotychczas przewidywano. Autorzy badania - naukowcy z konsorcjum EUROfusion, w tym dr Michał Poradziński z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy...
Czytaj więcejRozwój AI w syntezie jądrowej – IFPiLM z nowym projektem badawczym
12-09-2024

Konsorcjum EUROfusion, wspierając postępy w badaniach nad energią z syntezy jądrowej, uruchomiło 15 nowych projektów badawczych, które angażują ekspertów z dziedziny data science z całej Europy. Projekty te wykorzystają największy...
Czytaj więcejWizyta naukowców z IFPiLM na budowie tokamaka ITER
21-06-2024
W ostatnim czasie dr hab. Agata Chomiczewska, prof. IFPiLM, oraz dr inż. Natalia Wendler wzięły udział w międzynarodowej konferencji Plasma Surface Interaction in Controlled Fusion Devices PSI-26 w Marsylii, podczas...
Czytaj więcejIFPiLM na Kongresie "Nauka dla Społeczeństwa"
19-06-2024

W dniach 9-10 czerwca 2024 roku w Auli Wielkiej Politechniki Warszawskiej odbył się 2. Kongres "Nauka dla Społeczeństwa" pod hasłem "Tak nauka w Polsce wpływa na życie każdego człowieka". Instytut...
Czytaj więcejPodsumowanie 17. edycji Letniej Szkoły Fizyki Plazmy w Kudowie-Zdroju
18-06-2024

Zakończyła się 17. edycja Letniej Szkoły Fizyki Plazmy Kudowa Summer School „Towards Fusion Energy”. W wydarzeniu zorganizowanym przez Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) w dniach 3-7 czerwca 2024...
Czytaj więcejDwa projekty badawcze NCN dla pracowników naukowych IFPiLM
17-06-2024

Dwa projekty zgłoszone przez pracowników IFPiLM, które znalazły się na rezerwowej liście w konkursach OPUS 25 i Preludium 22, otrzymały dofinansowanie. Sfinansowanie dodatkowych projektów badawczych w konkursach było możliwe dzięki zwiększeniu...
Czytaj więcejZapraszamy na stoisko IFPiLM podczas Pikniku Naukowego 15 czerwca w Warszawie!
12-06-2024

Najbliższa edycja Pikniku Naukowego odbędzie się w sobotę, 15 czerwca 2024 roku, na PGE Narodowym w Warszawie. Temat przewodni wydarzenia: Nie do wiary! Na stoisku Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy...
Czytaj więcejZaproszenie na 2. edycję Kongresu „Nauka dla Społeczeństwa” z udziałem IFPiLM
04-06-2024

W dniach 9-10 czerwca 2024 roku na terenie Politechniki Warszawskiej odbędzie się 2. Kongres „Nauka dla Społeczeństwa”. Honorowy patronat nad wydarzeniem objęli Minister Nauki i Urząd Patentowy RP. Kongres odbywa...
Czytaj więcejInformacje ze Świata
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Igniting the future: Breakthroughs in inertial confinement Fusion
25-07-2025

In December 2022, the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (USA) marked a historic milestone in fusion science: an experiment produced 3.15 MJ of fusion energy from 2.05 MJ of laser...
Czytaj więcejWendelstein 7-X sets new fusion performance records
04-06-2025

On May 22, 2025, the Wendelstein 7-X (W7-X) stellarator at the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP) in Greifswald concluded its latest experimental campaign with a major success: a...
Czytaj więcejEuropean tokamak sets new fusion plasma record
20-02-2025

On February 12, 2025, the WEST tokamak, located at CEA Cadarache in southern France, set a new world record by sustaining fusion plasma for 1,337 seconds, or over 22 minutes....
Czytaj więcejDebata Parlamentu Europejskiego na temat energii ze syntezy jądrowej
27-01-2025

20 stycznia Parlament Europejski zorganizował swoją pierwszą debatę na temat energii z syntezy jądrowej, zatytułowaną „Zasilanie przyszłości Europy – Rozwój przemysłu syntezy jądrowej na rzecz niezależności energetycznej i innowacji”. Podczas...
Czytaj więcejDr. Gianfranco Federici appointed as the new EUROfusion Programme Manager
17-12-2024
At the 49th General Assembly held in Barcelona, December 2024, Dr. Gianfranco Federici was elected as the new Programme Manager of EUROfusion. He succeeds Prof. Ambrogio Fasoli, who will return...
Czytaj więcejEUROfusion and F4E join forces for Europe’s fusion future
16-12-2024

EUROfusion and Fusion for Energy (F4E) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to advance fusion research and development in Europe. This agreement reinforces cooperation in...
Czytaj więcejJohn J. Hopfield and Geoffrey E. Hinton awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics
08-10-2024

John J. Hopfield and Geoffrey E. Hinton have been awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics "for foundational discoveries and inventions that enable machine learning with artificial neural networks." The Nobel...
Czytaj więcejWendelstein 7-X begins new experimental campaign
10-09-2024

The Wendelstein 7-X, the world’s most advanced stellarator, is launching a new experimental campaign after a year of intensive maintenance and upgrades. This phase, known as OP2.2, begins on 10...
Czytaj więcejITER's New Project Baseline: A Robust Path to Fusion Energy Research
04-07-2024

On 3 July, ITER Director-General Pietro Barabaschi presented the new project baseline, under evaluation by the ITER Organization's governing body. This plan aims to ensure a robust start to scientific...
Czytaj więcejITER Council Presents Updated Project Baseline
21-06-2024

The ITER Council convened this week for its 34th meeting, where nearly 100 attendees reviewed significant updates to the project baseline. The proposed changes aim to optimize the overall project...
Czytaj więcejInaugural of ITER public-private fusion workshop
04-04-2024

Dear fusion colleagues, As many of you will have heard by now, ITER will be hosting a first-ever workshop to engage with private sector fusion initiatives at the end of May,...
Czytaj więcejNew Fusion Energy World Record at JET | Press Conference Highlights
09-02-2024

On 8 February 2024, EUROfusion, in collaboration with the UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA), proudly announced a new world record for the highest amount of fusion energy ever produced in...
Czytaj więcejLead the change: apply to become a Young Energy Ambassador
01-02-2024

Are you a young professional contributing to the energy transition? The European Sustainable Energy Week (EUSEW) invites you to apply for its Young Energy Ambassadorship. EUSEW is committed to empowering the leaders of tomorrow,...
Czytaj więcejLooking for 5 Monaco-ITER Fellows
23-01-2024

The recruitment campaign for 2024-2026 Monaco-ITER Postdoctoral Fellowships has opened. We are looking for top candidates with an excellent track record of creativity and accomplishment. Research possibilities exist in many areas...
Czytaj więcejWendelstein 7-X Call for Proposals OP 2.2 (Sep. 2024 to Dec. 2024) and OP 2.3 (Feb. 2025 to May 2025)
03-01-2024

For the preparation of the experimental programme of OP 2.2 and OP 2.3, we are pleased to invite you to submit experimental proposals. Submission of proposals will be possible in...
Czytaj więcejEurope and Japan celebrate breakthrough in paving the way for fusion energy
01-12-2023

The prospect of harnessing fusion energy is closer. The successful operation of JT-60SA, the most powerful experimental device to date, built by Europe and Japan, is a landmark achievement for...
Czytaj więcejFirst plasma was successfully generated at JT-60SA
26-10-2023

A momentous achievement in the field of nuclear fusion has been accomplished by a collaborative team of engineers from Europe and Japan. They have successfully generated tokamak plasma for the...
Czytaj więcejThe Nobel Prize in Physics 2023
03-10-2023
Pierre Agostini, Ferenc Krausz and Anne L’Huillier are the winners of this year's Nobel Prize in Physics. It was awarded "for experimental methods that generate attosecond pulses of light for...
Czytaj więcejUS Lab Replicates Fusion Ignition Breakthrough
08-08-2023
The US National Ignition Facility (NIF) has achieved fusion ignition once again, building on its landmark 2022 success. This achievement, powered by hydrogen within a diamond capsule, signifies a major...
Czytaj więcejNew Programme Manager Elect announced by EUROfusion
20-07-2023
Professor Ambrogio Fasoli became the new EUROfusion Programme Manager Elect. The decision was made by EUROfusion General Assembly at the meeting on 18 July 2023. His tenure will officially commence...
Czytaj więcejHuge growth ahead? Fusion supply chain report
07-06-2023

From a survey of 26 private fusion companies and 34 supplier companies, the Fusion Industry Association—a US-registered non-profit independent trade association for the acceleration of the arrival of fusion power—predicts a...
Czytaj więcejEarly-career engineers encouraged to apply now for the 2024 EUROfusion Engineering Grants
19-04-2023

EUROfusion has launched the call for applications for the 2024 EUROfusion Engineering Grants (EEGs). These grants will provide funding for up to twenty outstanding early-career engineers to conduct research projects starting in...
Czytaj więcejApply to the JT-60SA International Fusion School
10-04-2023

The new JT-60SA International Fusion School (JIFS), jointly funded and organized by Japan's National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology (QST) and EUROfusion, aims to prepare the next generation of fusion physicists and engineers...
Czytaj więcejXcitech IFMIF-DONES School on Science and Technology
20-03-2023

The Xcitech course is an advanced course primarily aimed at young scientists and engineers at the graduate and post-graduate level who are currently working or interested in the area of fusion technology. It is...
Czytaj więcejFusion Industry School announced
17-03-2023

The Fusion Centre for Doctoral Training (CDT) and the UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) have worked with the fusion community to prepare a two-week program created to meet the needs of the emerging...
Czytaj więcejEUROfusion stands in solidarity with research in Ukraine
24-02-2023

Today, as we commemorate the anniversary of the invasion of Ukraine by Russia, the EUROfusion consortium stands in solidarity with our Ukrainian member and research colleagues. EUROfusion remains committed to supporting...
Czytaj więcejEight-minute production of plasma with gigajoule energy turnover at Wendelstein 7-X
23-02-2023

Another target has been achieved only recently by the W7-X researchers, namely they managed to acquire an energy turnover of 1.3 gigajoules in the device, which is 17 times higher...
Czytaj więcejThe Nobel Prize in Physics 2022
04-10-2022

Alain Aspect, John F. Clauser and Anton Zeilinger are the winners of this year's Nobel Prize in Physics. It was awarded “for experiments with entangled photons, establishing the violation of...
Czytaj więcejNew experiments for fusion energy record breaker JET
27-09-2022

A new wave of fusion energy experiments on UK Atomic Energy Authority’s record-breaking Joint European Torus (JET) started this month. EUROfusion researchers are using the famous JET machine to conduct a...
Czytaj więcejITER appoints new Director-General
21-09-2022
Pietro Barabaschi has become the next Director-General of the ITER Organization as a result of the unanimous choice of the Council from among finalist candidates. In the transition period Dr....
Czytaj więcejStarting power plant design
07-07-2022

At a livestreamed Horizon EUROfusion event in Brussels on 5 July 2022, EUROfusion celebrated the start of conceptual design activities for Europe's first demonstration fusion power plant DEMO. This first-of-a-kind...
Czytaj więcejCelebration of achieving a crucial assembly milestone in the ITER Project
17-05-2022

This month, we have witnessed the successful lifting and lowering into the machine well of the first sub-section of the ITER plasma chamber. The weight of the component is the...
Czytaj więcejBurning plasma achieved in inertial fusion at the National Ignition Facility
15-02-2022
Obtaining a burning plasma is a critical step towards self-sustaining fusion energy. A burning plasma is one in which the fusion reactions themselves are the primary source of heating in...
Czytaj więcejHistoric milestone reached by JET scientists
20-01-2022

Iconic fusion energy machine JET – which reaches controlled temperatures 10 times hotter than the core of the sun – completed its 100,000th live pulse last night. Weighing 2,800 tonnes, the...
Czytaj więcejHorizon Europe Grant Agreement signed
20-12-2021

15 December 2021 saw the EUROfusion consortium signing the Grant Agreement under Horizon Europe, the European Framework Programme from 2021 – 2027, in an aim to launch comprehensive R&D approach...
Czytaj więcejExhibition brings fusion power to the people of Marseille
25-10-2021

The European research consortium EUROfusion presents a game-based exhibition blending art, science and technology to explore fusion energy and get visitors' input on how fusion could fit into society. Fusion, Power...
Czytaj więcejNagroda Nobla z fizyki 2021
06-10-2021
Laureatami tegorocznej Nagrody Nobla z fizyki zostali Syukuro Manabe, Klaus Hasselmann i Giorgio Parisi. Nagrodę przyznano im „za przełomowy wkład w zrozumienie złożonych systemów fizycznych”. Manabe i Hasselmann zostali uhonorowani „za...
Czytaj więcejNational Ignition Facility experiment puts researchers at threshold of fusion ignition
16-08-2021

On Aug. 8, 2021, an experiment at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL’s) National Ignition Facility (NIF) made a significant step toward ignition, achieving a yield of more than 1.3 megajoules...
Czytaj więcej"Chinese artificial sun" proves to be the hottest
01-06-2021
It turned possible for the Chinese scientists from Hefei to achieve a plasma temperature of 120 million degrees Celsius for 101 seconds. Thus they set a new world record about...
Czytaj więcejA solution provided by the UK experimental results at MAST
31-05-2021

The exhaust system proved commercially effective for fusion power plants thanks to the UK Atomic Energy Authority’s new MAST Upgrade experiment at CCFE. Culham scientists performing testing applied the Super-X system...
Czytaj więcejPrecision under the microscope for plasma impurity behaviour study
02-04-2021
How to track impurities such as titanium, iron, nickel, copper or tungsten migrating throughout fusion plasmas? It is possible that tiny hand-made pellets manage to perform this task. The study...
Czytaj więcejASDEX Upgrade celebrating its 30 anniversary of generating plasma
29-03-2021

30 years ago, on 21 March 1991, the ASDEX Upgrade experimental device at Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP) in Germany generated its first plasma. The main aim of...
Czytaj więcejCompletion of the first phase of WEST operation
22-03-2021

The WEST experimental campaign which took place between the 27th of November and the 27th of January 2021 proved successful with testing of a significant number of ITER-like Plasma Facing...
Czytaj więcejFull design toroidal field reported successfully reached by JT-60SA
03-03-2021

The scientific world can boast about efficient energizing of the toroidal field magnet, which made it possible to attain its full magnetic field. Plasma inside the vessel will be generated...
Czytaj więcejPrototype of another ITER divertor proves successful thanks to efforts of the European team
10-02-2021
The team of engineers from the Research Instruments (RI), Germany, has successfully completed the ITER Inner-Vertical Target (IVT) prototype’s engineering phase. The very complex component was produced no matter how...
Czytaj więcejDEMO - the next step towards fusion energy production
07-01-2021

The recommendations of the DEMO expert panel will facilitate the implementation of the next step of the Roadmap aimed at the construction of the demonstration power plant. Review-based approach makes...
Czytaj więcejFirst plasma in the MAST spherical tokamak device
02-11-2020

We have recently seen the launch of the MAST Upgrade tokamak which produced the first plasma (the video is available on YouTube). This brings us closed to obtain safe low-carbon...
Czytaj więcejSoon we will witness a new experimental campaign on the WEST tokamak
29-10-2020

Similarly to the cycle of nature, winter is coming also in the field of science. Namely, the cool down of the 140 tons superconducting Toroidal Field magnet has started under...
Czytaj więcejEUROfusion joins Neutral Beam Test Facility
08-10-2020

A new Cooperation Agreement between the international ITER fusion project, the Italian Consorzio RFX and EUROfusion will allow European researchers from eight countries to join the Neutral Beam Test Facility...
Czytaj więcejThe assembly of the ITER experimental reactor has started
10-08-2020

Ten years after the start of construction in August 2010, ITER marked a new chapter in its long history. This historic moment was witnesses by distinguished guests, including French President...
Czytaj więcej








