
Zestaw obrazów 2019
zdjecie1.jpg
zdjecie2.jpg
zdjecie3.jpg
zdjecie4.jpg
zdjecie5.jpg
zdjecie6.jpg
2019_1.JPG
2019_2.JPG
2019_4.JPG
Światowe
 Scientists at JET, the world’s largest fusion energy research facility, have been deliberately melting parts of their own machine as they test materials for the fusion reactors of the future. These apparent acts of scientific vandalism are actually courageous experiments which have yielded valuable information for JET’s successor – the huge international ITER project being built in the south of France.
Scientists at JET, the world’s largest fusion energy research facility, have been deliberately melting parts of their own machine as they test materials for the fusion reactors of the future. These apparent acts of scientific vandalism are actually courageous experiments which have yielded valuable information for JET’s successor – the huge international ITER project being built in the south of France.
The experiments were requested by ITER, which is currently assessing what material should be used for its plasma-facing wall. To achieve fusion, gas is heated to over one hundred million degrees, at which temperature it becomes a plasma, similar to the sun. Plasma is held inside a magnetic chamber known as a tokamak. Of particular concern to researchers are bursts of turbulence on the edge of the plasma similar to solar flares, which can momentarily inflict on to small areas of the tokamak wall heat loads far greater than a blow torch.
JET scientists have been astonished by the machine’s faultless performance during the recent tests.
“There was a slight worry we would see uncontrolled, firework-like splashes of molten metal,” said Dr Gilles Arnoux, one of the scientific coordinators of the experiment, “and that might affect subsequent experiments. But it was a smooth melt; the plasma didn’t seem to notice. I was surprised at how little impact it had.”
The tests at JET involved subjecting a small area of deliberately misaligned tungsten wall tile to regulated bursts of turbulent events. The peak temperature of the tile during the transient bursts was slowly increased until it exceeded tungsten’s melting point, 3422 degrees Celsius, to assess what effect molten tungsten might have on the operation of the plasma. In particular, it was feared that a melt event might contaminate the hydrogen-based plasma with tungsten and lead to a disruption – an uncontrolled energy dump from the plasma – which could lead to further surface melting in a fusion experiment as large as ITER.
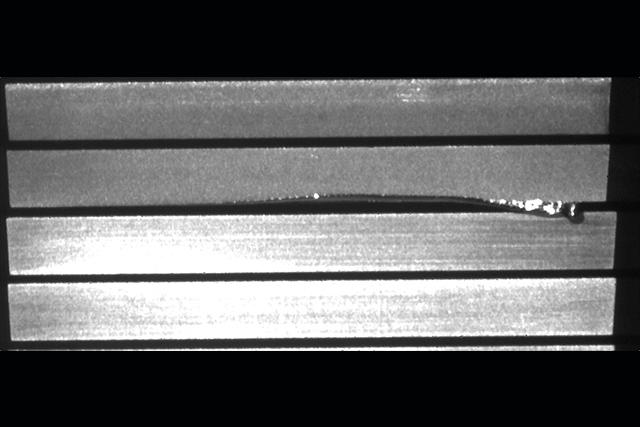
Instead, as shown in the picture, the molten tungsten moved smoothly to one end of the tile and formed a droplet, that grew with each additional plasma pulse. Curiously the molten metal did not run downwards – a result of the magnetic forces inside the tokamak – and, to the scientists’ relief, moved away from the hottest part of the plasma rather than being swept back into the exposed area. Subsequent experiments were performed without any interruption to proceedings.
Joining the JET team in the control room was the leader of ITER’s Divertor and Plasma Wall Interactions section, Dr Richard Pitts, who has been involved throughout the planning of the experiment.
Dr Pitts said: “It has been a great success and has achieved what it set out to do: to demonstrate that repetitive, fast transient heat pulses pushing tungsten over the melt threshold for just a millisecond or two each time, do not drive melt splashing nor do they appear to have any observable effect on the core plasma. It seems that we can broadly understand what we have seen on the basis of complex computer simulations describing the melt dynamics and thus our confidence is increased in the extrapolations we make for the behaviour to expect on ITER, which use the same computer codes. These results are extremely significant for the choice which ITER is preparing to make regarding the use of tungsten.”
Despite the early optimism much analysis remains to be done. The full story will not be known until mid 2014, when JET’s current run of experiments concludes and the melted tile can be removed and analysed.
Source: EFDA
 The team constructing the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) requested their colleagues operating UK’s tokamak JET to expose the machine to extreme loads to find the best materials for ITER’s plasma facing wall.
The team constructing the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) requested their colleagues operating UK’s tokamak JET to expose the machine to extreme loads to find the best materials for ITER’s plasma facing wall.
“There was a slight worry we would see uncontrolled, firework-like splashes of molten metal and that might affect subsequent experiments,” said Dr Gilles Arnoux, one of the scientific coordinators of the experiment. “But it was a smooth melt; the plasma didn’t seem to notice. I was surprised at how little impact it had.”
The tests at JET involved subjecting a small area of a deliberately misaligned tungsten wall tile to regulated bursts of turbulent plasma. During the experiment, the exposed tile was heated up to peak temperatures of 3422° C, to allow the researchers assessing what affect molten tungsten might have on the plasma.
The team’s biggest concern was the melt event could result in contamination of the hydrogen-based plasma with tungsten, which would cause disruption and uncontrolled energy dump of the plasma. Such situation would lead to further melting of the surface, which might become detrimental to the equipment's safety.
However, the molten material moved smoothly to one end of the tile during the experiment, forming a droplet that grew with each additional plasma pulse. Surprisingly, the droplet did not run downwards, but moved away from the hottest part of the plasma instead, due to magnetic forces inside the tokamak.
“It has been a great success and has achieved what it set out to do,” said Dr Richard Pitts, the leader of ITER’s Divertor and Plasma Wall Interactions section, who joined the JET team during the experiment.
“It seems that we can broadly understand what we have seen on the basis of complex computer simulations describing the melt dynamics and thus our confidence is increased in the extrapolations we make for the behaviour to expect on ITER,” he said, adding the results are extremely significant for the ITER team, currently considering the use of tungsten for the construction of ITER.
To achieve fusion inside a tokamak, gas needs to be heated to more than one hundred million ° C, at which temperature it turns into sun-like plasma. Of particular concern to researchers are bursts of turbulence on the edge of the plasma similar to solar flares, which can momentarily inflict heat loads far greater than a blow torch on small areas of the tokamak wall.
The experiments at JET, which is currently the world’s biggest operating tokamak, will continue until mid-2014
Source: E&T
 For the first time ever, a Toroidal Field (TF) coil full-size super-conducting prototype of the double pancake (DP) is being manufactured and the first step of the manufacturing process, winding, has been completed at the beginning of August. This milestone, which was carried out at the ASG premises in La Spezia, Italy, follows the production of the winding line.
For the first time ever, a Toroidal Field (TF) coil full-size super-conducting prototype of the double pancake (DP) is being manufactured and the first step of the manufacturing process, winding, has been completed at the beginning of August. This milestone, which was carried out at the ASG premises in La Spezia, Italy, follows the production of the winding line.
The ITER device will operate with a system of superconducting magnets which relies on the Toroidal Field coils, the Central Solenoid, the Poloidal Field coils and the Correction coils. F4E is responsible for procuring ten TF coils (Japan will contribute an additional nine TF coils) – “D” shaped coils which will be operated with an electrical current of 68,000 amps, in order to produce the magnetic field which confines and holds the plasma in place in the ITER tokamak. Each TF coil weighs about 300 tons and it is about 16.5 m tall and 9.5 m wide.
Each TF coil contains in total seven double pancakes which produce the magnetic field (two DPs which contain cable-in-conduit conductors measuring 450 m, and five DPs where the conductors measure 750 m in length). Each double pancake is composed of a of conductor length which carries the electrical current, and of a stainless steel D-shaped plate called a radial plate, which holds and mechanically supports the conductor through groves machined on both sides along a spiral trajectory. The conductor is composed of about 1000 superconducting and copper wires cabled inside a 2 mm thick round stainless steel jacket 43.7 mm in diameter.
The winding of the DP, the most challenging component in the TF coil from the manufacturing point of view, consists of bending the conductor length along a D-shaped double spiral trajectory. As it is necessary that the double pancake conductor fits precisely inside the radial plate groove, it is vital to control the trajectory of the conductor in the double pancake and the trajectory of the groove in the radial plate with an extremely high accuracy. In particular, the trajectory of the conductor must be controlled with an accuracy as high as 0.01%, and this is why the winding line utilises a numerically controlled bending unit as well as laser-based technology to measure the position and the dimensions of the conductor. The winding takes place in an environment with a controlled temperature of 20 °C +/-1 C, and at an average speed of 5 m of conductor length per hour.
A consortium composed of Italian company ASG and Spanish companies Iberdrola and Elytt is responsible for the manufacturing of the prototype as well as the future actual double pancakes. With the winding of the prototype now completed, other manufacturing steps are needed: the DP will be heat-treated at 650° C in a specially constructed inert atmosphere oven, then electrically insulated and finally transferred into the grooves of the stainless steel radial plates. After assembly and the application of electrical insulation on the outside of the radial plate, the module is finally impregnated with special radiation resistant epoxy resin thus forming the prototype double pancake module. This work is scheduled to be completed by the beginning of next year and will then allow for the prototype to be tested by being cooled to -77 K in order to assess the effect of the low temperature. It will then be cut in sections in order to analyse the quality of the impregnation of the insulation of the superconducting conductor.
Source: F4E
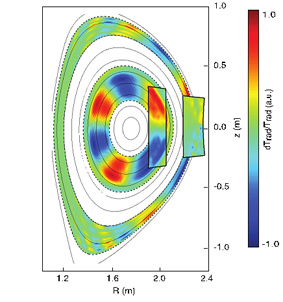 A key issue for the development of fusion energy to generate electricity is the ability to confine the superhot, charged plasma gas that fuels fusion reactions in magnetic devices called tokamaks. This gas is subject to instabilities that cause it to leak from the magnetic fields and halt fusion reactions.
A key issue for the development of fusion energy to generate electricity is the ability to confine the superhot, charged plasma gas that fuels fusion reactions in magnetic devices called tokamaks. This gas is subject to instabilities that cause it to leak from the magnetic fields and halt fusion reactions.
Now a recently developed imaging technique can help researchers improve their control of instabilities. The new technique, developed by physicists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), the University of California-Davis and General Atomics in San Diego, provides new insight into how the instabilities respond to externally applied magnetic fields.
This technique, called Electron Cyclotron Emission Imaging (ECEI) and successfully tested on the DIII-D tokamak at General Atomics, uses an array of detectors to produce a 2D profile of fluctuating electron temperatures within the plasma. Standard methods for diagnosing plasma temperature have long relied on a single line of sight, providing only a 1D profile. Results of the ECEI technique, recently reported in the journal Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, could enable researchers to better model the response of confined plasma to external magnetic perturbations that are applied to improve plasma stability and fusion performance.
Source: phys.org
 Early Saturday morning we fired a Deuterium-Tritium gas-filled Diamond capsule on the NIF. The laser used all 192 beams and delivered 1.24 Megajoules of ultraviolet laser light to the drive Hohlraum at a 350 Terawatts peak power in an ~10 nanosecond pulse.
Early Saturday morning we fired a Deuterium-Tritium gas-filled Diamond capsule on the NIF. The laser used all 192 beams and delivered 1.24 Megajoules of ultraviolet laser light to the drive Hohlraum at a 350 Terawatts peak power in an ~10 nanosecond pulse.
Excellent data was obtained and for the first time ever we observed a DT neutron yield over 1E15 (early results are coming in at ~1.8E15) or approximately 5,000 Joules of neutron energy.
The yield is about twice the record we have ever produced.
Even better, the Yield over Clean, a measure of the quality of the implosion, was also very impressive and this was done with a relatively low laser energy, low laser power and low implosion velocity! Although much work remains, this bodes well for the first layered diamond experiments planned for September.
It's hard not to feel encouraged by the progress we've made with great new and planned diagnostic capabilities, promising results with diamond and high foot experiments, a team that is working extremely well together, and a go forward plan that, by and large, is well supported by the community.
Informacje z Kraju
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
GO4FUSION Capability Mapping Survey – termin do 21 stycznia 2026 r.
15-01-2026
Projekt GO4FUSION zaprasza europejskie organizacje działające w obszarze energii termojądrowej do udziału w badaniu Capability Mapping Survey (mapowanie kompetencji i potencjału). Celem ankiety jest przygotowanie kompleksowego przeglądu europejskich kompetencji w zakresie...
Czytaj więcejIFPiLM wspiera podopiecznych Centrum TPD "Helenów"
22-12-2025

Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego (IFPiLM) od wielu lat angażuje się w działania na rzecz podopiecznych Centrum Rehabilitacji, Edukacji i Opieki TPD „Helenów” w Warszawie. 9 grudnia...
Czytaj więcejNaukowcy z IFPiLM uczestniczyli w kampanii eksperymentalnej na laserze GEKKO XII
20-11-2025

W dniach 10–14 listopada 2025 r. zespół naukowców z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego (IFPiLM) w składzie: dr hab. Katarzyna Batani, dr Hanna Marchenko oraz dr...
Czytaj więcejZgłoś swój udział w 18. edycji Letniej Szkoły Fizyki Plazmy!
07-11-2025

Zapraszamy do udziału w 18. edycji Letniej Szkoły Fizyki Plazmy – Kudowa Summer School "Towards Fusion Energy", która odbędzie się 8–12 czerwca 2026 r. w Kudowie-Zdroju. Organizatorem wydarzenia jest Instytut...
Czytaj więcejOdszedł prof. dr hab. Zbigniew Kłos
05-11-2025
Z głębokim żalem zawiadamiamy, że 3 listopada 2025 roku zmarł prof. dr hab. Zbigniew Kłos – wybitny naukowiec, współtwórca i wieloletni dyrektor Centrum Badań Kosmicznych PAN. W latach 2008–2011 Profesor pełnił...
Czytaj więcejKonsultacje Strategic Research & Innovation Agenda (SRIA) – do 5 listopada 2025 r.
17-10-2025
Europejska Platforma Interesariuszy Fuzji Jądrowej (European Fusion Stakeholder Platform), powołana w ramach projektu GO4FUSION CSA, pracuje nad przygotowaniem Strategicznego Programu na rzecz przyszłego partnerstwa publiczno-prywatnego (PPP) w obszarze energii termojądrowej....
Czytaj więcejIFPiLM wziął udział w drugim spotkaniu technicznym w ramach projektu DONES Con-P1
17-10-2025
Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) wziął udział w drugim spotkaniu technicznym realizowanym w ramach projektu DONES Consolidation Phase 1 (DONES ConP1) współfinansowanego przez Komisję Europejską w ramach programu...
Czytaj więcejProf. Jan Badziak z IFPiLM w gronie World's Top 2% Scientists
15-10-2025
Prof. dr hab. Jan Badziak z Zakładu Fizyki Plazmy Laserowej i Gęstej Plazmy Namagnetyzowanej w Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy znalazł się na prestiżowej liście Stanford/Elsevier Top 2% Scientists...
Czytaj więcej29. Festiwal Nauki z udziałem IFPiLM
10-10-2025

Podczas 29. Festiwalu Nauki w Warszawie, który odbył się w dniach 19–28 września 2025 roku, naukowcy z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy przeprowadzili lekcje dla uczniów klas 7–8 szkół...
Czytaj więcejPLASMA 2025 i 20-lecie Asocjacji Euratom–IFPiLM – podsumowanie wydarzenia
26-09-2025

W dniach 15–19 września 2025 roku w Warszawie odbyła się międzynarodowa konferencja naukowa PLASMA 2025 – International Conference on Research and Application of Plasmas, poświęcona badaniom, diagnostyce i zastosowaniom plazmy....
Czytaj więcejZ żalem żegnamy Profesora Jerzego Wołowskiego
25-09-2025

Z głębokim smutkiem przyjęliśmy wiadomość o śmierci prof. dr. hab. Jerzego Wołowskiego (1936–2025), wybitnego fizyka, wieloletniego pracownika Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy, mentora i przyjaciela. Jerzy Wołowski urodził się w...
Czytaj więcej20. rocznica Asocjacji Euratom-IFPiLM (CeNTE): Obchody dwóch dekad koordynacji badań nad syntezą jądrową
16-09-2025

19 września 2025 roku, podczas międzynarodowej Konferencji PLASMA 2025 odbywającej się w Warszawie i poświęconej badaniom, diagnostyce i zastosowaniom plazmy, IFPiLM będzie obchodzić 20. rocznicę koordynacji badań nad syntezą jądrową...
Czytaj więcejUdział IFPiLM w 49. Zjeździe Fizyków Polskich w Katowicach
13-09-2025
Podczas 49. Zjazdu Fizyków Polskich, który odbył się w dniach 5–11 września 2025 roku w Katowicach, Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) był reprezentowany zarówno w gronie prelegentów, jak...
Czytaj więcejProf. Agata Chomiczewska powołana na zastępcę dyrektora ds. naukowych w IFPiLM
03-09-2025

Informujemy, że Minister Energii Miłosz Motyka z dniem 1 września 2025 roku powołał dr hab. Agatę Chomiczewską na stanowisko zastępcy dyrektora do spraw naukowych w Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej...
Czytaj więcejPubliczna obrona rozprawy doktorskiej mgr. inż. Przemysława Tchórza - 21 sierpnia 2025 roku
15-07-2025
Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego zaprasza na publiczną obronę rozprawy doktorskiej mgr. inż. Przemysława Tchórza, która odbędzie się 21 sierpnia 2025 r. (czwartek) o godz. 12:00...
Czytaj więcejZawiadomienie o publicznej obronie rozprawy doktorskiej mgr. inż. Przemysława Tchórza
10-07-2025
Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego zaprasza na publiczną obronę rozprawy doktorskiej mgr. inż. Przemysława Tchórza, która odbędzie się 21 sierpnia 2025 r. (czwartek) o godz. 12:00...
Czytaj więcejHistoryczne wydarzenie – Rada Naukowa Instytutu nadała stopień doktora habilitowanego
10-07-2025
Po raz pierwszy w historii Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego (IFPiLM) Rada Naukowa podjęła uchwałę w sprawie nadania stopnia doktora habilitowanego. Było to możliwe dzięki uzyskaniu...
Czytaj więcejNowy skład Rady Oddziału Fizyki Plazmy Europejskiego Towarzystwa Fizycznego
04-07-2025

W pierwszym kwartale 2025 roku przeprowadzono wybory do Rady Oddziału Fizyki Plazmy Europejskiego Towarzystwa Fizycznego (EPS Plasma Physics Division). Sześciu kandydatów z najwyższą liczbą głosów zostało wybranych do Zarządu, a...
Czytaj więcejOgłoszenie o postępowaniu konkursowym na stanowisko zastępcy dyrektora do spraw naukowych
30-06-2025
OGŁOSZENIE o postępowaniu konkursowym na stanowisko zastępcy dyrektora do spraw naukowychw Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego w Warszawie Działając na podstawie art. 27 ust. 1 ustawy z dnia...
Czytaj więcejZawiadomienie o kolokwium habilitacyjnym
30-06-2025
ZAWIADOMIENIE o kolokwium habilitacyjnym Dnia 4 lipca 2025 r. o godz. 11:00 odbędzie się kolokwium habilitacyjne dr Katarzyny Batani (Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy) w trybie hybrydowym. Określenie osiągnięcia będącego podstawą ubiegania...
Czytaj więcejNaukowcy z IFPiLM dzielą się wiedzą specjalistyczną w zakresie fuzji na 10. Kongresie Przemysłu Jądrowego Europy Środkowej i Wschodniej 2025
12-06-2025
Naukowcy z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) – dr inż. Natalia Wendler i dr inż. Paweł Gąsior – wzięli udział w panelu dyskusyjnym podczas 10. Kongresu Przemysłu Jądrowego...
Czytaj więcejIFPiLM na 3. Kongresie "Nauka dla Społeczeństwa"
29-05-2025

W dniach 25-26 maja 2025 roku w Dużej Auli Politechniki Warszawskiej odbyła się 3. edycja Kongresu "Nauka dla Społeczeństwa". Celem wydarzenia było pokazanie, że nauka to nie tylko praca w...
Czytaj więcejZaproszenie na 3. edycję Kongresu „Nauka dla Społeczeństwa” z udziałem IFPiLM
22-05-2025

W dniach 25–26 maja 2025 roku na terenie Politechniki Warszawskiej odbędzie się 3. edycja Kongresu „Nauka dla Społeczeństwa” – wydarzenia, które pokazuje, że nauka to nie tylko praca w laboratoriach,...
Czytaj więcejZapraszamy na 28. Piknik Naukowy!
06-05-2025

Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) zaprasza w sobotę, 10 maja, na swoje stoisko podczas 28. Pikniku Naukowego, organizowanego przez Polskie Radio i Centrum Nauki Kopernik. Tegoroczna edycja wydarzenia,...
Czytaj więcejPorozumienie o współpracy pomiędzy IFPiLM a Narodowym Muzeum Techniki
18-04-2025

17 kwietnia 2025 roku zostało podpisane porozumienie o współpracy pomiędzy Narodowym Muzeum Techniki (NMT) a Instytutem Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM). Uroczyste spotkanie, z udziałem dyrektor IFPiLM dr hab. Moniki...
Czytaj więcejPolscy i francuscy naukowcy łączą siły w badaniach nad fuzją jądrową
28-03-2025

W dniach 24-25 marca 2025 roku w siedzibach IFJ PAN i Instytutu Francuskiego w Krakowie odbyło się spotkanie polsko-francuskie, którego celem była wymiana doświadczeń oraz rozwój współpracy naukowej między instytucjami...
Czytaj więcejGiełda Prac Magisterskich i Doktorskich w ELI ERIC
21-03-2025

Giełda Prac Magisterskich i Doktorskich w ELI ERIC (Extreme Light Infrastructure, European Research Infrastructure Consortium) Do: Magistrantów, Doktorantów i ich Promotorów, Miłośników ultrakrótkich impulsowych laserów dużej mocy i ich zastosowań, Entuzjastów egzotycznych zjawisk indukowanych...
Czytaj więcejOtwarcie likwidacji fundacji "Wspieranie Międzynarodowego Centrum Gęstej, Namagnesowanej Plazmy"
14-03-2025

OGŁOSZENIE O OTWARCIU LIKWIDACJI FUNDACJI "WSPIERANIE MIĘDZYNARODOWEGO CENTRUM GĘSTEJ, NAMAGNESOWANEJ PLAZMY"wraz z wezwaniem wierzycieli Podaje się do publicznej wiadomości, że w dniu 20 stycznia 2025 r. Rada Fundacji "WSPIERANIE MIĘDZYNARODOWEGO CENTRUM GĘSTEJ, NAMAGNESOWANEJ...
Czytaj więcejZapraszamy na międzynarodową konferencję na temat badań, diagnostyki i zastosowań plazmy – PLASMA 2025!
13-03-2025

Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) zaprasza na międzynarodową konferencję na temat badań, diagnostyki i zastosowań plazmy – PLASMA 2025, która odbędzie się w dniach 15-19 września 2025 roku...
Czytaj więcejSzkolenie online: "Granty na Eurogranty – jak przygotować skuteczny wniosek"
10-03-2025

Horyzontalne Punkty Kontaktowe Polska Wschodnia i Polska Centralna zapraszają na szkolenie online pt. "Granty na Eurogranty – jak przygotować skuteczny wniosek". "Granty na Eurogranty" to inicjatywa Polskiej Agencji Rozwoju Przedsiębiorczości (PARP)...
Czytaj więcejEksperymentalna sesja badawcza w laboratorium Plasma-Focus PF1000U w ramach współpracy ICDMP
27-02-2025
W dniach 10–21 lutego 2025 r. w laboratorium Plasma-Focus PF-1000U przeprowadzono sesję eksperymentalną, w której, obok zespołu IFPiLM, uczestniczył trzyosobowy zespół pracowników naukowych z Politechniki Praskiej (ČVUT), kierowany przez prof....
Czytaj więcejPaliwa termojądrowe wykryte podczas demonstracji lasera na JET
11-02-2025

Naukowcy i inżynierowie z ośmiu krajów, w tym z Polski, z powodzeniem zademonstrowali zastosowanie laserów na tokamaku Joint European Torus (JET), udowadniając, że jest to opłacalna technologia pomiaru retencji paliwa...
Czytaj więcejPracownik IFPiLM nominowany do tytułu Osobowość Roku w kategorii Nauka
24-01-2025
Pracownik badawczo-techniczny mgr inż. Olgierd Cichorek z Laboratorium Plazmowych Napędów Satelitarnych w IFPiLM został nominowany do tytułu Osobowość Roku 2024 w kategorii Nauka. Kapituła Redakcji „Polskiej Metropolii Warszawskiej”, „Echa Dnia” i...
Czytaj więcejProf. Monika Kubkowska nowym dyrektorem IFPiLM
02-01-2025

Z przyjemnością informujemy, że Pani Minister Przemysłu Marzena Czarnecka z dniem 1 stycznia 2025 roku powołała dr hab. Monikę Kubkowską na stanowisko dyrektora Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im....
Czytaj więcejChristian Perez von Thun członkiem grupy ITPA w obszarze Pedestal & Edge Physics
31-12-2024
Dr Christian Perez von Thun z Zakładu Badań Plazmy Termojądrowej w Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy został członkiem grupy International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA) w obszarze Pedestal & Edge...
Czytaj więcejPrzemysław Tchórz nowym co-Leaderem grupy roboczej WG2 w ramach COST Action PROBONO
23-12-2024

Przemysław Tchórz z Zakładu Fizyki i Zastosowań Plazmy Laserowej w Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy został mianowany w ramach konkursu co-Leaderem grupy roboczej WG2: Experiments: Proton boron and Towards...
Czytaj więcejIFPiLM wspiera podopiecznych z Centrum Rehabilitacji, Edukacji i Opieki TPD „Helenów”
20-12-2024

Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) od lat angażuje się w pomoc podopiecznym z Centrum Rehabilitacji, Edukacji i Opieki TPD „Helenów” w Warszawie. W 2024 roku wsparcie Instytutu miało...
Czytaj więcejWykład naukowców z IFPiLM podczas Śląskiego Festiwalu Nauki w Katowicach!
25-11-2024

Dr hab. Agata Chomiczewska i dr inż. Natalia Wendler z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) wygłoszą wykład pt. „Synteza jądrowa – przełomowe wyniki badań, które mogą zmienić przyszłość...
Czytaj więcejModernizacja diagnostyki PHA i udział naukowców z IFPiLM w nowej kampanii na W7-X
24-10-2024

Zespół naukowców z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) przeprowadził znaczącą modernizację diagnostyki PHA (pulse-height analyzer), która jest obecnie aktywnie wykorzystywana na stellaratorze Wendelstein 7-X w ramach kampanii OP.2.2,...
Czytaj więcejOGŁOSZENIE
22-10-2024
Ogłoszenie o postępowaniu konkursowym na stanowisko dyrektora w Instytucie Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy im. Sylwestra Kaliskiego Działając na podstawie art. 24 ust. 2 ustawy z dnia 30 kwietnia 2010 r....
Czytaj więcejOd powstania lasera do fuzji jądrowej – zapraszamy na wykład dr Agnieszki Zaraś-Szydłowskiej
21-10-2024

Zapraszamy na wykład dr Agnieszki Zaraś-Szydłowskiej z Zakładu Fizyki i Zastosowań Plazmy Laserowej. Temat wystąpienia: Od powstania lasera do fuzji jądrowej: technologia, zastosowania i najnowsze osiągnięcia w świecie laserów Spotkanie odbędzie się...
Czytaj więcejZapraszamy na wykład o plazmowych napędach kosmicznych
27-09-2024

Zapraszamy na wykład mgr. inż. Macieja Jakubczaka z Laboratorium Plazmowych Napędów Satelitarnych. Temat wystąpienia: Nadniebny rejs - historia i przyszłość plazmowych napędów kosmicznych. Spotkanie odbędzie się 3 października 2024 r. o godz....
Czytaj więcejEksperymenty z mieszaniną paliw fuzyjnych stabilizują plazmę w reaktorach fuzyjnych
25-09-2024
Przyszłe elektrownie termojądrowe mogą doświadczać mniejszych strat energii w spalanej plazmie niż dotychczas przewidywano. Autorzy badania - naukowcy z konsorcjum EUROfusion, w tym dr Michał Poradziński z Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy...
Czytaj więcejRozwój AI w syntezie jądrowej – IFPiLM z nowym projektem badawczym
12-09-2024

Konsorcjum EUROfusion, wspierając postępy w badaniach nad energią z syntezy jądrowej, uruchomiło 15 nowych projektów badawczych, które angażują ekspertów z dziedziny data science z całej Europy. Projekty te wykorzystają największy...
Czytaj więcejWizyta naukowców z IFPiLM na budowie tokamaka ITER
21-06-2024
W ostatnim czasie dr hab. Agata Chomiczewska, prof. IFPiLM, oraz dr inż. Natalia Wendler wzięły udział w międzynarodowej konferencji Plasma Surface Interaction in Controlled Fusion Devices PSI-26 w Marsylii, podczas...
Czytaj więcejIFPiLM na Kongresie "Nauka dla Społeczeństwa"
19-06-2024

W dniach 9-10 czerwca 2024 roku w Auli Wielkiej Politechniki Warszawskiej odbył się 2. Kongres "Nauka dla Społeczeństwa" pod hasłem "Tak nauka w Polsce wpływa na życie każdego człowieka". Instytut...
Czytaj więcejPodsumowanie 17. edycji Letniej Szkoły Fizyki Plazmy w Kudowie-Zdroju
18-06-2024

Zakończyła się 17. edycja Letniej Szkoły Fizyki Plazmy Kudowa Summer School „Towards Fusion Energy”. W wydarzeniu zorganizowanym przez Instytut Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy (IFPiLM) w dniach 3-7 czerwca 2024...
Czytaj więcejDwa projekty badawcze NCN dla pracowników naukowych IFPiLM
17-06-2024

Dwa projekty zgłoszone przez pracowników IFPiLM, które znalazły się na rezerwowej liście w konkursach OPUS 25 i Preludium 22, otrzymały dofinansowanie. Sfinansowanie dodatkowych projektów badawczych w konkursach było możliwe dzięki zwiększeniu...
Czytaj więcejZapraszamy na stoisko IFPiLM podczas Pikniku Naukowego 15 czerwca w Warszawie!
12-06-2024

Najbliższa edycja Pikniku Naukowego odbędzie się w sobotę, 15 czerwca 2024 roku, na PGE Narodowym w Warszawie. Temat przewodni wydarzenia: Nie do wiary! Na stoisku Instytutu Fizyki Plazmy i Laserowej Mikrosyntezy...
Czytaj więcejZaproszenie na 2. edycję Kongresu „Nauka dla Społeczeństwa” z udziałem IFPiLM
04-06-2024

W dniach 9-10 czerwca 2024 roku na terenie Politechniki Warszawskiej odbędzie się 2. Kongres „Nauka dla Społeczeństwa”. Honorowy patronat nad wydarzeniem objęli Minister Nauki i Urząd Patentowy RP. Kongres odbywa...
Czytaj więcejInformacje ze Świata
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Igniting the future: Breakthroughs in inertial confinement Fusion
25-07-2025

In December 2022, the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (USA) marked a historic milestone in fusion science: an experiment produced 3.15 MJ of fusion energy from 2.05 MJ of laser...
Czytaj więcejWendelstein 7-X sets new fusion performance records
04-06-2025

On May 22, 2025, the Wendelstein 7-X (W7-X) stellarator at the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP) in Greifswald concluded its latest experimental campaign with a major success: a...
Czytaj więcejEuropean tokamak sets new fusion plasma record
20-02-2025

On February 12, 2025, the WEST tokamak, located at CEA Cadarache in southern France, set a new world record by sustaining fusion plasma for 1,337 seconds, or over 22 minutes....
Czytaj więcejDebata Parlamentu Europejskiego na temat energii ze syntezy jądrowej
27-01-2025

20 stycznia Parlament Europejski zorganizował swoją pierwszą debatę na temat energii z syntezy jądrowej, zatytułowaną „Zasilanie przyszłości Europy – Rozwój przemysłu syntezy jądrowej na rzecz niezależności energetycznej i innowacji”. Podczas...
Czytaj więcejDr. Gianfranco Federici appointed as the new EUROfusion Programme Manager
17-12-2024
At the 49th General Assembly held in Barcelona, December 2024, Dr. Gianfranco Federici was elected as the new Programme Manager of EUROfusion. He succeeds Prof. Ambrogio Fasoli, who will return...
Czytaj więcejEUROfusion and F4E join forces for Europe’s fusion future
16-12-2024

EUROfusion and Fusion for Energy (F4E) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to advance fusion research and development in Europe. This agreement reinforces cooperation in...
Czytaj więcejJohn J. Hopfield and Geoffrey E. Hinton awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics
08-10-2024

John J. Hopfield and Geoffrey E. Hinton have been awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics "for foundational discoveries and inventions that enable machine learning with artificial neural networks." The Nobel...
Czytaj więcejWendelstein 7-X begins new experimental campaign
10-09-2024

The Wendelstein 7-X, the world’s most advanced stellarator, is launching a new experimental campaign after a year of intensive maintenance and upgrades. This phase, known as OP2.2, begins on 10...
Czytaj więcejITER's New Project Baseline: A Robust Path to Fusion Energy Research
04-07-2024

On 3 July, ITER Director-General Pietro Barabaschi presented the new project baseline, under evaluation by the ITER Organization's governing body. This plan aims to ensure a robust start to scientific...
Czytaj więcejITER Council Presents Updated Project Baseline
21-06-2024

The ITER Council convened this week for its 34th meeting, where nearly 100 attendees reviewed significant updates to the project baseline. The proposed changes aim to optimize the overall project...
Czytaj więcejInaugural of ITER public-private fusion workshop
04-04-2024

Dear fusion colleagues, As many of you will have heard by now, ITER will be hosting a first-ever workshop to engage with private sector fusion initiatives at the end of May,...
Czytaj więcejNew Fusion Energy World Record at JET | Press Conference Highlights
09-02-2024

On 8 February 2024, EUROfusion, in collaboration with the UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA), proudly announced a new world record for the highest amount of fusion energy ever produced in...
Czytaj więcejLead the change: apply to become a Young Energy Ambassador
01-02-2024

Are you a young professional contributing to the energy transition? The European Sustainable Energy Week (EUSEW) invites you to apply for its Young Energy Ambassadorship. EUSEW is committed to empowering the leaders of tomorrow,...
Czytaj więcejLooking for 5 Monaco-ITER Fellows
23-01-2024

The recruitment campaign for 2024-2026 Monaco-ITER Postdoctoral Fellowships has opened. We are looking for top candidates with an excellent track record of creativity and accomplishment. Research possibilities exist in many areas...
Czytaj więcejWendelstein 7-X Call for Proposals OP 2.2 (Sep. 2024 to Dec. 2024) and OP 2.3 (Feb. 2025 to May 2025)
03-01-2024

For the preparation of the experimental programme of OP 2.2 and OP 2.3, we are pleased to invite you to submit experimental proposals. Submission of proposals will be possible in...
Czytaj więcejEurope and Japan celebrate breakthrough in paving the way for fusion energy
01-12-2023

The prospect of harnessing fusion energy is closer. The successful operation of JT-60SA, the most powerful experimental device to date, built by Europe and Japan, is a landmark achievement for...
Czytaj więcejFirst plasma was successfully generated at JT-60SA
26-10-2023

A momentous achievement in the field of nuclear fusion has been accomplished by a collaborative team of engineers from Europe and Japan. They have successfully generated tokamak plasma for the...
Czytaj więcejThe Nobel Prize in Physics 2023
03-10-2023
Pierre Agostini, Ferenc Krausz and Anne L’Huillier are the winners of this year's Nobel Prize in Physics. It was awarded "for experimental methods that generate attosecond pulses of light for...
Czytaj więcejUS Lab Replicates Fusion Ignition Breakthrough
08-08-2023
The US National Ignition Facility (NIF) has achieved fusion ignition once again, building on its landmark 2022 success. This achievement, powered by hydrogen within a diamond capsule, signifies a major...
Czytaj więcejNew Programme Manager Elect announced by EUROfusion
20-07-2023
Professor Ambrogio Fasoli became the new EUROfusion Programme Manager Elect. The decision was made by EUROfusion General Assembly at the meeting on 18 July 2023. His tenure will officially commence...
Czytaj więcejHuge growth ahead? Fusion supply chain report
07-06-2023

From a survey of 26 private fusion companies and 34 supplier companies, the Fusion Industry Association—a US-registered non-profit independent trade association for the acceleration of the arrival of fusion power—predicts a...
Czytaj więcejEarly-career engineers encouraged to apply now for the 2024 EUROfusion Engineering Grants
19-04-2023

EUROfusion has launched the call for applications for the 2024 EUROfusion Engineering Grants (EEGs). These grants will provide funding for up to twenty outstanding early-career engineers to conduct research projects starting in...
Czytaj więcejApply to the JT-60SA International Fusion School
10-04-2023

The new JT-60SA International Fusion School (JIFS), jointly funded and organized by Japan's National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology (QST) and EUROfusion, aims to prepare the next generation of fusion physicists and engineers...
Czytaj więcejXcitech IFMIF-DONES School on Science and Technology
20-03-2023

The Xcitech course is an advanced course primarily aimed at young scientists and engineers at the graduate and post-graduate level who are currently working or interested in the area of fusion technology. It is...
Czytaj więcejFusion Industry School announced
17-03-2023

The Fusion Centre for Doctoral Training (CDT) and the UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) have worked with the fusion community to prepare a two-week program created to meet the needs of the emerging...
Czytaj więcejEUROfusion stands in solidarity with research in Ukraine
24-02-2023

Today, as we commemorate the anniversary of the invasion of Ukraine by Russia, the EUROfusion consortium stands in solidarity with our Ukrainian member and research colleagues. EUROfusion remains committed to supporting...
Czytaj więcejEight-minute production of plasma with gigajoule energy turnover at Wendelstein 7-X
23-02-2023

Another target has been achieved only recently by the W7-X researchers, namely they managed to acquire an energy turnover of 1.3 gigajoules in the device, which is 17 times higher...
Czytaj więcejThe Nobel Prize in Physics 2022
04-10-2022

Alain Aspect, John F. Clauser and Anton Zeilinger are the winners of this year's Nobel Prize in Physics. It was awarded “for experiments with entangled photons, establishing the violation of...
Czytaj więcejNew experiments for fusion energy record breaker JET
27-09-2022

A new wave of fusion energy experiments on UK Atomic Energy Authority’s record-breaking Joint European Torus (JET) started this month. EUROfusion researchers are using the famous JET machine to conduct a...
Czytaj więcejITER appoints new Director-General
21-09-2022
Pietro Barabaschi has become the next Director-General of the ITER Organization as a result of the unanimous choice of the Council from among finalist candidates. In the transition period Dr....
Czytaj więcejStarting power plant design
07-07-2022

At a livestreamed Horizon EUROfusion event in Brussels on 5 July 2022, EUROfusion celebrated the start of conceptual design activities for Europe's first demonstration fusion power plant DEMO. This first-of-a-kind...
Czytaj więcejCelebration of achieving a crucial assembly milestone in the ITER Project
17-05-2022

This month, we have witnessed the successful lifting and lowering into the machine well of the first sub-section of the ITER plasma chamber. The weight of the component is the...
Czytaj więcejBurning plasma achieved in inertial fusion at the National Ignition Facility
15-02-2022
Obtaining a burning plasma is a critical step towards self-sustaining fusion energy. A burning plasma is one in which the fusion reactions themselves are the primary source of heating in...
Czytaj więcejHistoric milestone reached by JET scientists
20-01-2022

Iconic fusion energy machine JET – which reaches controlled temperatures 10 times hotter than the core of the sun – completed its 100,000th live pulse last night. Weighing 2,800 tonnes, the...
Czytaj więcejHorizon Europe Grant Agreement signed
20-12-2021

15 December 2021 saw the EUROfusion consortium signing the Grant Agreement under Horizon Europe, the European Framework Programme from 2021 – 2027, in an aim to launch comprehensive R&D approach...
Czytaj więcejExhibition brings fusion power to the people of Marseille
25-10-2021

The European research consortium EUROfusion presents a game-based exhibition blending art, science and technology to explore fusion energy and get visitors' input on how fusion could fit into society. Fusion, Power...
Czytaj więcejNagroda Nobla z fizyki 2021
06-10-2021
Laureatami tegorocznej Nagrody Nobla z fizyki zostali Syukuro Manabe, Klaus Hasselmann i Giorgio Parisi. Nagrodę przyznano im „za przełomowy wkład w zrozumienie złożonych systemów fizycznych”. Manabe i Hasselmann zostali uhonorowani „za...
Czytaj więcejNational Ignition Facility experiment puts researchers at threshold of fusion ignition
16-08-2021

On Aug. 8, 2021, an experiment at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL’s) National Ignition Facility (NIF) made a significant step toward ignition, achieving a yield of more than 1.3 megajoules...
Czytaj więcej"Chinese artificial sun" proves to be the hottest
01-06-2021
It turned possible for the Chinese scientists from Hefei to achieve a plasma temperature of 120 million degrees Celsius for 101 seconds. Thus they set a new world record about...
Czytaj więcejA solution provided by the UK experimental results at MAST
31-05-2021

The exhaust system proved commercially effective for fusion power plants thanks to the UK Atomic Energy Authority’s new MAST Upgrade experiment at CCFE. Culham scientists performing testing applied the Super-X system...
Czytaj więcejPrecision under the microscope for plasma impurity behaviour study
02-04-2021
How to track impurities such as titanium, iron, nickel, copper or tungsten migrating throughout fusion plasmas? It is possible that tiny hand-made pellets manage to perform this task. The study...
Czytaj więcejASDEX Upgrade celebrating its 30 anniversary of generating plasma
29-03-2021

30 years ago, on 21 March 1991, the ASDEX Upgrade experimental device at Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP) in Germany generated its first plasma. The main aim of...
Czytaj więcejCompletion of the first phase of WEST operation
22-03-2021

The WEST experimental campaign which took place between the 27th of November and the 27th of January 2021 proved successful with testing of a significant number of ITER-like Plasma Facing...
Czytaj więcejFull design toroidal field reported successfully reached by JT-60SA
03-03-2021

The scientific world can boast about efficient energizing of the toroidal field magnet, which made it possible to attain its full magnetic field. Plasma inside the vessel will be generated...
Czytaj więcejPrototype of another ITER divertor proves successful thanks to efforts of the European team
10-02-2021
The team of engineers from the Research Instruments (RI), Germany, has successfully completed the ITER Inner-Vertical Target (IVT) prototype’s engineering phase. The very complex component was produced no matter how...
Czytaj więcejDEMO - the next step towards fusion energy production
07-01-2021

The recommendations of the DEMO expert panel will facilitate the implementation of the next step of the Roadmap aimed at the construction of the demonstration power plant. Review-based approach makes...
Czytaj więcejFirst plasma in the MAST spherical tokamak device
02-11-2020

We have recently seen the launch of the MAST Upgrade tokamak which produced the first plasma (the video is available on YouTube). This brings us closed to obtain safe low-carbon...
Czytaj więcejSoon we will witness a new experimental campaign on the WEST tokamak
29-10-2020

Similarly to the cycle of nature, winter is coming also in the field of science. Namely, the cool down of the 140 tons superconducting Toroidal Field magnet has started under...
Czytaj więcejEUROfusion joins Neutral Beam Test Facility
08-10-2020

A new Cooperation Agreement between the international ITER fusion project, the Italian Consorzio RFX and EUROfusion will allow European researchers from eight countries to join the Neutral Beam Test Facility...
Czytaj więcejThe assembly of the ITER experimental reactor has started
10-08-2020

Ten years after the start of construction in August 2010, ITER marked a new chapter in its long history. This historic moment was witnesses by distinguished guests, including French President...
Czytaj więcej








